







InstElectric - Electricity

Beschreibung von InstElectric - Electricity
Tool to support the calculation of electrical installations that will allow the user (designer / electrician / technician) to perform electrical calculations easily and quickly.
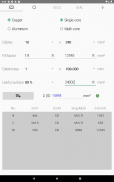
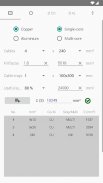
· Dimensioning complete of low voltage circuits with the most frequent installation methods
· Phase cable size, neutral, protective conductor
· Criteria based on the admissible current of the cable, voltage drop and overcurrent protection
· Designation of the most used cables.
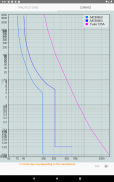
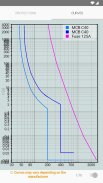
· Circuits with automatic circuit breaker until In = 4000 A (Ir rating setting), maximum fuse In = 1600 A (gG type), maximum 12 conductors parallel per phase, maximum size 630 mm²
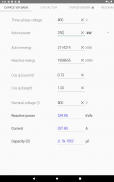
· Estimate of the maximum short-circuit current (simplified method)
· Forecast of loads of a building destined to houses with several sections: dwellings, common services, commercial premises/offices and garage with/without infrastructure for recharging electric vehicles
· Reactive power of the capacitor bank for the compensation of the power factor (cos φ) and capacity (µF) of the capacitors
· C/K Factor for automatic capacitor bank
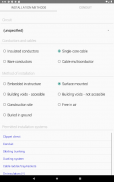
· Choice of installation system in the function of the circuit, cable and its situation
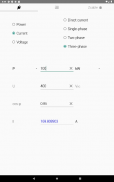
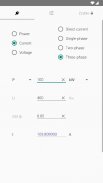
· Power in an unbalanced three-phase system
· Overvoltages due to loss of neutral conductor, earth fault and short circuit
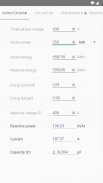
· Electricity parameters of a single-phase or three-phase (balanced)
· Transformer performance
· Secondary voltage of a transformer acoording to switch position
· Size of trays and conduits
· Conduits characteristics according to the installation method
· Conversions of wire sizes (mm²-awg) and conduits threads
Parameter settings for calculations:
· Constants (voltages, conductivity, temperatures, etc.) that affect electrical calculations
· Protections (circuit breakers and fuses)
· Selection of minimum rate for circuit-breakers with regulation and maximum cable size for multi-conductor grouping per phase
· Method estimation of the reactance
· Conductivity of the conductor depending on the current of the circuit (constant, according to the expected current, maximum cable temperature)
· Use reduction factors by grouping cables/circuits
· Use of factors of diversity/utilization
· Reference documents: IEC Standards, REBT (sp), Technical Application Guide, (UE) 2016/364
IN NO CASE SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT OR INDIRECT DAMAGES AS A RESULT OF THE CORRECT OR INCORRECT USE OF THE APPLICATION
Tool zur Unterstützung der Berechnung von elektrischen Installationen, mit dem der Benutzer (Designer / Elektriker / Techniker) elektrische Berechnungen einfach und schnell durchführen kann.
· Dimensionierung kompletter Niederspannungskreise mit den häufigsten Installationsmethoden
· Phasenleitungsgröße, Neutralleiter, Schutzleiter
· Kriterien basierend auf dem zulässigen Strom des Kabels, Spannungsabfall und Überstromschutz
· Bezeichnung der am häufigsten verwendeten Kabel.
· Stromkreise mit Sicherungsautomat bis In = 4000 A (Ir-Einstellung), maximale Sicherung In = 1600 A (Typ gG), maximal 12 Leiter parallel pro Phase, maximale Größe 630 mm²
· Schätzung des maximalen Kurzschlussstroms (vereinfachte Methode)
· Vorhersage der Lasten eines Gebäudes, das für Häuser mit mehreren Abschnitten bestimmt ist: Wohnungen, öffentliche Dienste, Geschäftsräume / Büros und eine Garage mit / ohne Infrastruktur zum Aufladen von Elektrofahrzeugen
· Blindleistung der Kondensatorbatterie zur Kompensation des Leistungsfaktors (cos φ) und der Kapazität (µF) der Kondensatoren
· C / K-Faktor für automatische Kondensatorbank
· Wahl des Installationssystems in Abhängigkeit von Stromkreis, Kabel und Lage
· Leistung in einem unsymmetrischen Dreiphasensystem
· Überspannungen durch Neutralleiterverlust, Erdschluss und Kurzschluss
· Stromparameter einphasig oder dreiphasig (symmetrisch)
· Transformatorleistung
· Sekundärspannung eines Transformators entsprechend der Schalterstellung
· Größe der Tabletts und Leitungen
· Eigenschaften der Leitungen entsprechend der Installationsmethode
· Umrechnung von Drahtstärken (mm²-awg) und Leitungsgewinden
Parametereinstellungen für Berechnungen:
· Konstanten (Spannungen, Leitfähigkeit, Temperaturen usw.), die die elektrischen Berechnungen beeinflussen
· Schutzvorrichtungen (Leistungsschalter und Sicherungen)
· Auswahl der Mindestrate für Leistungsschalter mit Regelung und der maximalen Kabelgröße für die Mehrleitergruppierung pro Phase
· Methodenschätzung der Reaktanz
· Leitfähigkeit des Leiters in Abhängigkeit vom Strom des Stromkreises (konstant, entsprechend dem zu erwartenden Strom, maximale Kabeltemperatur)
· Verwenden Sie Reduktionsfaktoren, indem Sie Kabel / Stromkreise gruppieren
· Verwendung von Faktoren der Vielfalt / Nutzung
· Referenzdokumente: IEC-Normen, REBT (sp), Technical Application Guide, (UE) 2016/364
IN KEINEM FALL HAFTET DER AUTOR FÜR DIREKTE ODER INDIREKTE SCHÄDEN, DIE AUS DER RICHTIGEN ODER FEHLERHAFTEN VERWENDUNG DER ANWENDUNG ENTSTEHEN
























